Methods
The NCDB was queried for men with newly diagnosed mPCa, all treated with ADT, with
complete datasets for RT, surgery, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, Gleason score, and
Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score. OS was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method, log-rank
test, Cox proportionalhazards models, and propensity score-matched analyses.
Results
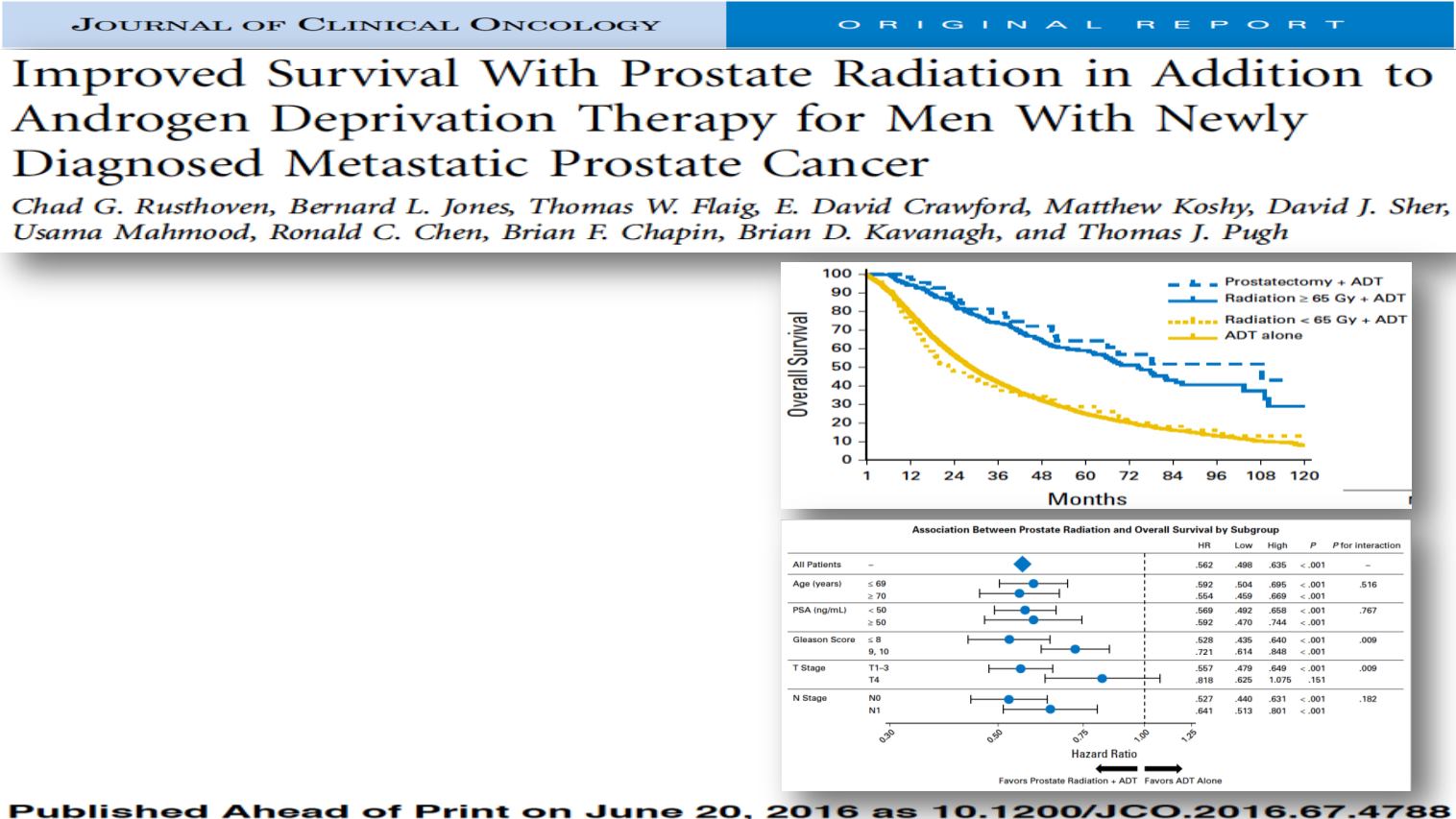
From2004 to 2012, 6,382menwithmPCawere identified, including 538 (8.4%) receiving prostate
RT. At a median follow-up of 5.1 years, the addition of prostate RT to ADT was associated with
improved OS on univariate (P , .001) and multivariate analysis (hazard ratio, 0.624; 95% CI,
0.551 to 0.706; P , .001) adjusted for age, year, race, comorbidity score, PSA level, Gleason
score, T stage, N stage, chemotherapy administration, treating facility, and insurance status.
Propensity score analysis with matched baseline characteristics demonstrated superiormedian
(55 v 37months) and 5-year OS (49% v 33%) with prostate RT plus ADT compared with ADT
alone (P, .001). Landmark analyses limited to long-term survivors of $1, $3, and $5 years
demonstrated improved OS with prostate RT in all subsets (all P , .05). Secondary analyses
comparing the survival outcomes for patients treated with therapeutic dose RT plus ADT versus
prostatectomy plus ADT during the same time interval demonstrated no significant differences
in OS, whereas both therapies were superior to ADT alone.
Conclusion
In this large contemporary analysis, men with mPCa receiving prostate RT and ADT lived
substantially longer than men treated with ADT alone. Prospective trials evaluating local
therapies for mPCa are warranted.


